A analysis group on the College of Bologna has recognized, for the primary time, the particular location and genomic context the place DNA breaks happen as a result of inhibition of the topoisomerase I, a protein essential for a lot of organic processes in cells. The outcomes, revealed within the journal Science Advances, might result in vital advances within the growth of recent most cancers remedies.
Probably the most vital features of topoisomerase I is the regulation of DNA supercoiling. In reality, the DNA molecule is often folded again on itself a number of occasions to suit contained in the cell nucleus and is just ‘relaxed’ at sure occasions similar to throughout replication and transcription.
This elementary function in cell life makes topoisomerase I an vital goal for most cancers therapies: its inhibition results in DNA strand breaks, stopping the replication of diseased cells. This breakdown mechanism was the main target of the investigation led by Alma Mater researchers.
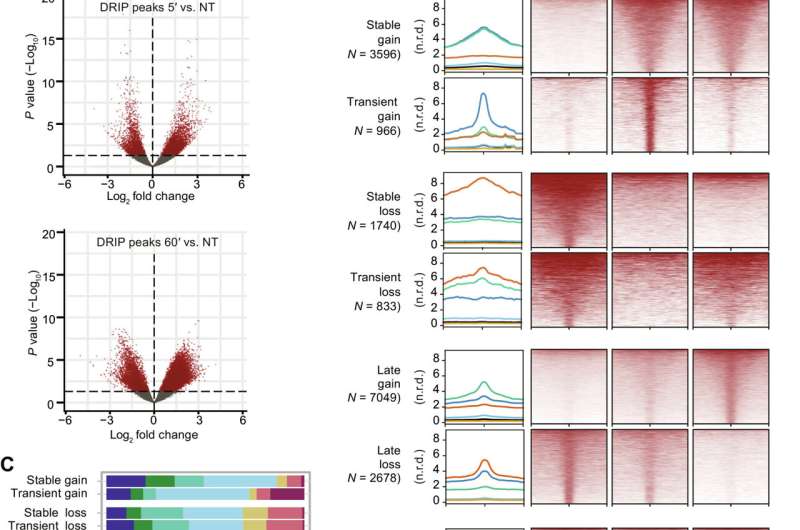
“Utilizing genome sequencing applied sciences, we have been in a position to map double-strand breaks in DNA throughout your complete human genome and combine this information with genomic maps of different vital components concerned within the DNA transcription course of,” explains Giovanni Capranico, professor on the Division of Pharmacy and Biotechnology on the College of Bologna, who coordinated the research.
“By integrating and bioinformatically analyzing this information, we have been in a position for the primary time to outline the situation and genomic context through which DNA topoisomerase I inhibition-induced breaks happen. We additionally found that this breakage mechanism solely happens in the beginning of the cell cycle part, when DNA replication happens.”
In brief, the outcomes describe a brand new mechanism by which topoisomerase inhibition induces DNA harm and genomic instability in most cancers cells, a discovery that would result in new most cancers therapies.
The research was carried out by the Genomic Instability in Most cancers Analysis Group of the Division of Pharmacy and Biotechnology on the College of Bologna.
The analysis group below the management of Professor Giovanni Capranico and contains Renée C. Duardo, Jessica Marinello, Marco Russo, Sara Morelli, Simona Pepe and Federico Guerra. Throughout the research, Renée C. Duardo (then a Ph.D. pupil) frolicked overseas on the Andalusian Molecular Biology and Regenerative Medication Centre (CABIMER) and the College of Seville, below the supervision of Professors Andrés Aguilera and Belen Gomez Gonzalez.
Extra info:
Renée C. Duardo et al, Human DNA topoisomerase I poisoning causes R loop–mediated genome instability attenuated by transcription issue IIS, Science Advances (2024). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adm8196
Quotation:
Newly found mechanism halts tumor cell replication (2024, August 8)
retrieved 8 August 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-08-newly-mechanism-halts-tumor-cell.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.
