Romantic relationships and attraction amongst people have been the main focus of quite a few psychological and neuroscientific research. Whereas these research have unveiled a number of the neural and psychological processes related to romantic bonding, many questions on their underlying mechanisms stay unanswered.
Researchers on the Hebrew College of Jerusalem lately carried out a research exploring how physiological synchrony between people contributes to their romantic bonding. Their findings, revealed in Communications Psychology, recommend that better synchrony with one other particular person can increase the extent to which they’re perceived as romantically engaging.
“We aimed to find a organic mechanism that impacts mate choice in people and the way the power to synchronize can signify health,” Dr. Shir Atzil, co-author of the paper, instructed Medical Xpress. “We hypothesized that the power to synchronize stems from elementary sensorimotor skills and that this adaptability could be perceived as useful in romantic contexts.”
The thought behind this latest research by Dr. Atzil and her colleagues is that physiological synchrony between people might contribute to their mutual attraction. The rationale behind that is that synchronized physiological states between two individuals can facilitate the regulation of bodily programs, finally enabling extra fulfilling interactions between them.
“Since we hypothesized that the complicated social habits of synchrony is definitely anchored in domain-general sensorimotor options, we measured individuals’ skill to synchronize, each socially, the place we measured the individuals’ skill for physiological synchrony with their companions throughout a date, and in a sensorimotor synchronization job, the place we measured the individuals’ skill to synchronize their finger faucet to a metronome bit,” Dr. Atzil defined.
“We additionally acquired attraction rankings for all of our individuals.”
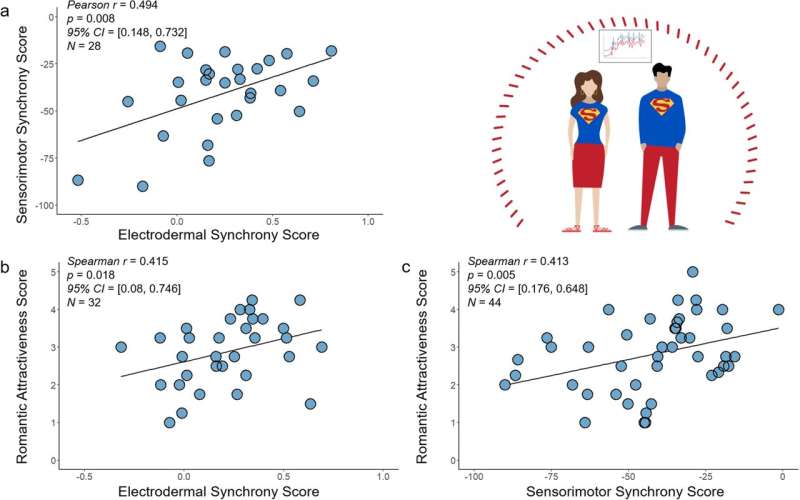
The researchers first carried out an preliminary on-line experiment involving 144 individuals. These individuals have been requested to look at brief movies by which a male and a feminine actor interacted with one another, exhibiting both a low or excessive physiological and behavioral synchrony.
After watching this video, they have been requested to price the attractiveness of the female and male actors. As well as, they have been requested to price how attracted they felt the male actor was to the feminine actress, and vice versa. Lastly, as a final query, they have been requested how behaviorally synchronized they believed the 2 characters within the video to be.
The researchers discovered that better synchrony between the actors within the movies elevated the attractiveness rankings offered by the research individuals. Dr. Atzil and her colleagues then carried out a follow-up research in particular person, involving 48 individuals.
These individuals have been requested to work together with potential companions in a velocity courting experiment. Every interplay lasted 5 minutes and as soon as it was full, individuals have been requested to price the attractiveness of the particular person that they had simply dated with and full a tapping job designed to measure their synchronization.
Through the velocity dates, the researchers collected physiological knowledge from the individuals utilizing a wearable system known as the Empatica E4 wristband. This system measured the activation of the sympathetic nervous system, the secretion of sweat and modifications in electrodermal exercise.
“We see that the power to synchronize is secure throughout duties and throughout companions. Some individuals are tremendous synchronizers, and tremendous synchronizers are persistently rated as extra engaging,” Dr. Atzil mentioned.
Total, the findings gathered by these researchers recommend that better physiological synchrony with one other particular person will increase the extent to which this particular person is perceived as romantically engaging. This remark confirms their preliminary speculation, suggesting that synchrony with others might have evolutionary and cognitive benefits, which might make extra interesting as potential mates.
The latest analysis led by Dr. Atzil, together with colleagues Matan Cohen and Prof. Merav Ahissar, might quickly pave the best way for additional research exploring how physiological synchrony impacts romantic attraction. Collectively, these works might result in new fascinating discoveries concerning the complicated processes underpinning mate choice amongst people.
“A very powerful discovering of this research is that synchrony is a site basic particular person aptitude, which signifies romantic attraction,” Dr. Atzil added. “We plan to check and characterize tremendous synchronizers and their neural, behavioral, and physiological profile.”
Extra data:
M. Cohen et al, Social and nonsocial synchrony are interrelated and romantically engaging, Communications Psychology (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s44271-024-00109-1
© 2024 Science X Community
Quotation:
Examine hyperlinks social and non-social synchrony to romantic attractiveness (2024, July 6)
retrieved 6 July 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-07-links-social-synchrony-romantic.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.
