Thousands and thousands of adults have atrial fibrillation—an irregular beating of the higher chambers of the guts that yields elevated danger of coronary heart failure, stroke and demise. Many genetic mutations within the growing fetus can result in grownup atrial fibrillation, together with mutations that shorten the large protein titin in cardiac muscle cells.
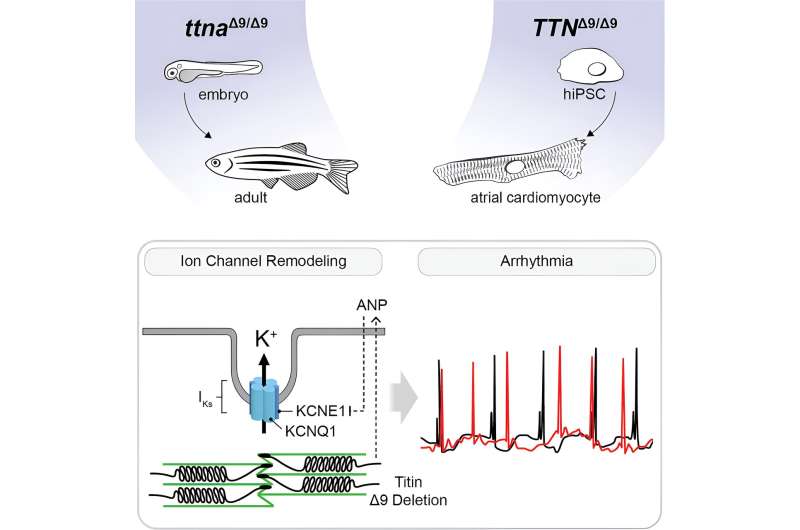
Now, in a examine in zebrafish and human coronary heart muscle cells, researchers present {that a} tiny deletion within the A-band of titin—the lack of simply 9 amino acids out of greater than 27,000 to 35,000 amino acids of an intact titin protein—causes a developmental defect within the embryonic coronary heart that results in grownup arrhythmia.
The paper titled “Transient titin-dependent ventricular defects throughout growth result in grownup atrial arrhythmia and impaired contractility” is revealed within the journal iScience.
Researchers on the College of Alabama at Birmingham Marnix E. Heersink Faculty of Medication and on the College of Illinois Chicago discovered that the small inside deletion in titin that led to developmental abnormalities brought about sudden ion channel reworking in coronary heart muscle cells, creating an elevated potassium ion present known as Iks (pronounced “eye okay s”).
Strikingly, researchers discovered that pharmacologically blocking the altered Iks present improved atrial contractility within the 9 amino acid-deletion zebrafish embryos, and it equally improved contractility and prevented atrial fibrillation within the 9 amino acid-deletion human cells.
“This work has potential scientific implications for each pediatric and grownup sufferers,” mentioned Ankur Saxena, Ph.D., a UAB affiliate professor within the Division of Cell, Developmental and Integrative Biology.
“With titin serving as an electromechanical bridge between sarcomeric buildings and ion channels, growing drug remedies focusing on ion channel reworking could restore and keep sinus rhythm and enhance contractility, in addition to enhance the long-term consequence for sufferers.”
Saxena and Dawood Darbar, M.D., of the College of Illinois Chicago, are corresponding authors of the examine.
In finding out the results of the nine-amino acid deletion in zebrafish embryos and adults in addition to human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived atrial cardiomyocytes, the UAB and College of Illinois Chicago researchers found that zebrafish embryos homozygous for the nine-amino acid deletion confirmed a transient discount in ventricular operate, with smaller measurement, decreased contraction and slower blood circulation; nevertheless, the ventricle recovered inside a couple of days.
In distinction, embryonic and grownup mutant zebrafish had persistent atrial enlargement, and grownup mutant zebrafish had atrial fibrillation. In each the grownup zebrafish atria and human atrial cardiomyocytes, mutated titin yielded sarcomeric disorganization and decreased contraction.
The researchers subsequent explored how transient ventricular and chronic atrial embryonic defects mechanistically led to grownup atrial fibrillation.
Earlier work had proven that the hormone atrial natriuretic peptide, or ANP, is overexpressed in response to ventricular dysfunction by way of an elevated Iks, generally known as the sluggish delayed rectifier potassium present.
In settlement with that, co-first authors of the examine, Xinghang Jiang, a postdoctoral fellow within the UAB Division of Cell, Developmental, and Integrative Biology, and Olivia T. Ly, College of Illinois Chicago, and colleagues discovered aberrant ANP expression and modifications within the expression of proteins that type the potassium channel in each the mutant zebrafish atria and human cardiomyocytes.
Moreover, knockdown of ANP improved atrial contraction, and voltage clamp experiments confirmed potassium channel reworking, with considerably greater peak Iks density.
“Elucidating the molecular mechanisms by which developmental defects result in elevated danger of atrial fibrillation in adults has been difficult, with uncommon recognized examples,” the researchers wrote within the examine.
“Right here, to discover the connection between developmental defects and the pathogenesis of atrial fibrillation, we deleted simply 9 amino acids in titin’s A-band and recognized an sudden function for this big protein in mediating each ion channel-dependent reworking and impaired atrial contractility.
“Notably, early cardiac dysfunction and restoration result in aberrant ANP expression and ion channel reworking, with potential implications for the way refined structural mutations would possibly trigger subclinical abnormalities that result in atrial fibrillation in maturity.”
Extra info:
Xinghang Jiang et al, Transient titin-dependent ventricular defects throughout growth result in grownup atrial arrhythmia and impaired contractility, iScience (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110395
Quotation:
Tiny deletion in coronary heart muscle protein linked to long-term results on grownup atrial fibrillation (2024, July 25)
retrieved 25 July 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-07-tiny-deletion-heart-muscle-protein.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.
